(Figure:source ISO25010 document)
The material of ISO is unfortunate not open. But since quality matters and ISO 25010 is used heavily for managing quality aspects within business IT systems a short overview.
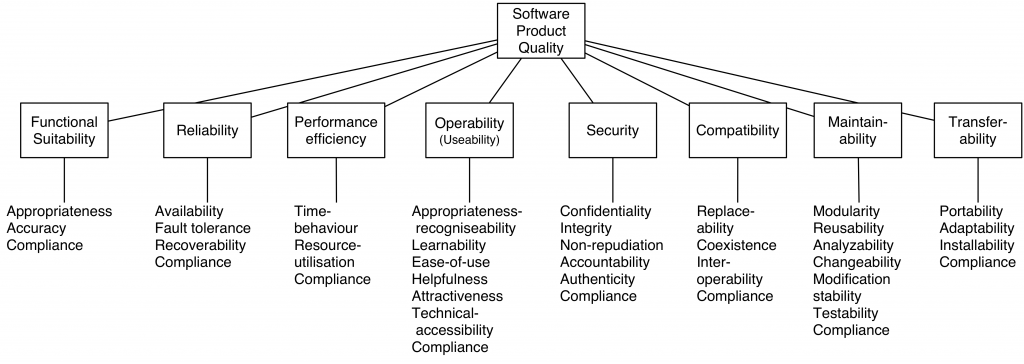
Functionality
Functionality: A set of attributes that bear on the existence of a set of functions and their specified properties. The functions are those that satisfy stated or implied needs.
- Functional suitability: Degree to which a product or system provides functions that meet stated and implied needs when used underspecified conditions.
- Functional completeness : Degree to which the set of functions covers all the specified tasks and user objectives.
- Functional correctness : Degree to which a product or system provides the correct results with the needed degree of precision.
- Functional appropriateness : Degree to which the functions facilitate the accomplishment of specified tasks and objectives.
Reliability
Reliability: A set of attributes that bear on the capability of software to maintain its level of performance under stated conditions for a stated period of time. Attributes:
- Reliability:Degree to which a system, product or component performs specified functions under specified conditions for a specified period of time.
- Maturity : Degree to which a system, product or component meets needs for reliability under normal operation.
- Availability : Degree to which a system, product or component is operational and accessible when required for use.
- Fault tolerance : Degree to which a system, product or component operates as intended despite the presence of hardware or software faults.
- Recoverability : Degree to which, in the event of an interruption or a failure, a product or system can recover the data directly affected and re-establish the desired state of the system.
Performance Efficiency
A set of attributes that bear on the relationship between the level of performance of the software and the amount of resources used, under stated conditions.
- Performance efficiency: Performance relative to the amount of resources used under stated conditions.
- Time behaviour : Degree to which the response and processing times and throughput rates of a product or system, when performing its functions, meet requirements.
Resource utilization : Degree to which the amounts and types of resources used by a product or system, when performing its functions, meet requirements. - Capacity : Degree to which the maximum limits of a product or system parameter meet requirements.
Compatibility
Compatibility:Degree to which a product, system or component can exchange information with other products, systems or components, and/or perform its required functions, while sharing the same hardware or software environment.
- Co-existence : Degree to which a product can perform its required functions efficiently while sharing a common environment and resources with other products, without detrimental impact on any other product.
- Interoperability : Degree to which two or more systems, products or components can exchange information and use the information that has been exchanged.
Usability
Usability:Degree to which a product or system can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction in a specified context of use.
- Appropriateness recognizability : Degree to which users can recognize whether a product or system is appropriate for their needs.
- Learnability : Degree to which a product or system can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals of learning to use the product or system with effectiveness, efficiency, freedom from risk and satisfaction in a specified context of use.
- Operability : Degree to which a product or system has attributes that make it easy to operate and control.
- User error protection : Degree to which a system protects users against making errors.
- User interface aesthetics : Degree to which a user interface enables pleasing and satisfying interaction for the user.
- Accessibility : Degree to which a product or system can be used by people with the widest range of characteristics and capabilities to achieve a specified goal in a specified context of use.
Security
Security:Degree to which a product or system protects information and data so that persons or other products or systems have the degree of data access appropriate to their types and levels of authorization.
- Confidentiality : Degree to which a product or system ensures that data are accessible only to those authorized to have access.
- Integrity : Degree to which a system, product or component prevents unauthorized access to, or modification of, computer programs or data.
- Non-repudiation : Degree to which actions or events can be proven to have taken place, so that the events or actions cannot be repudiated later.
- Accountability : Degree to which the actions of an entity can be traced uniquely to the entity.
- Confidentiality : Degree to which a product or system ensures that data are accessible only to those authorized to have access.
- Authenticity : Degree to which the identity of a subject or resource can be proved to be the one claimed.
Maintainability
- Maintainability:Degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which a product or system can be modified by the intended maintainers.
- Modularity : Degree to which a system or computer program is composed of discrete components such that a change to one component has minimal impact on other components.
- Reusability :Degree to which an asset can be used in more than one system, or in building other assets.
- Analysability : Degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which it is possible to assess the impact on a product or system of an intended change to one or more of its parts, or to diagnose a product for deficiencies or causes of failures, or to identify parts to be modified.
- Modifiability : Degree to which a product or system can be effectively and efficiently modified without introducing defects or degrading existing product quality.
- Testability : Degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which test criteria can be established for a system, product or component and tests can be performed to determine whether those criteria have been met.
Transferability
- Portability:Degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which a system, product or component can be transferred from one hardware, software or other operational or usage environment to another
- Adaptability : Degree to which a product or system can effectively and efficiently be adapted for different or evolving hardware, software or other operational or usage environments.
- Installability : Degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which a product or system can be successfully installed and/or un-installed in a specified environment.
- Replaceability : Degree to which a product can replace another specified software product for the same purpose in the same environment.
Note that when you do a critical review on ISO20510 you will find that missing in ISO25010 is:
- Functional requirements
- Compliance (e.g. with laws, standards) requirements
- Documentation, Support and Training requirements and of course:
- Project Timing requirements
- Project Budget requirements